Nasal obstruction and deviated septum correction (Septoplasty)
Nasal obstruction and deviated septum correction (Septoplasty)
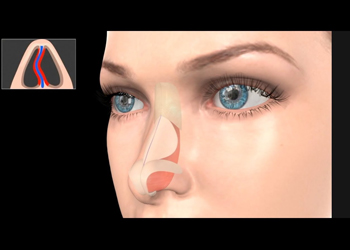
Nasal obstruction is often caused by a deviated septum — a condition where the cartilage and bone dividing the nasal passages are displaced. This can lead to difficulty breathing, snoring, sinus issues and reduced quality of life. Septoplasty straightens the septum, restores normal airflow and significantly improves nasal breathing.
Treatments Offered
Our approach includes a complete evaluation and precise surgical correction to ensure comfortable, long-lasting results:
-
Nasal Endoscopy: Detailed assessment of nasal passages, septal deviation and associated turbinate enlargement.
-
Medical Therapy (when indicated): Nasal sprays, antihistamines or decongestants for temporary relief before surgery.
-
Septoplasty: Surgical straightening of the deviated septum to improve nasal airflow and reduce blockage.
-
Endoscopic Septoplasty: Minimally invasive approach using an endoscope for precision and faster healing.
-
Turbinate Reduction (if required): Reducing enlarged turbinates to enhance breathing and prevent recurrence of obstruction.
Symptoms & Causes
You may need septoplasty if you experience:
-
Persistent nasal blockage on one or both sides
-
Snoring or disturbed sleep due to poor airflow
-
Frequent sinus infections or headaches linked to nasal obstruction
-
Nosebleeds caused by airflow irregularities or dryness
Causes include trauma, congenital deviation, previous surgery, turbinate hypertrophy or chronic inflammation. Nasal endoscopy and imaging help determine severity and plan treatment.
Postoperative Care & Recovery
Proper care after septoplasty ensures smooth healing and long-term success:
-
Avoid blowing your nose for 1–2 weeks to protect the surgical site
-
Use saline sprays to keep nasal passages moist and aid healing
-
Avoid heavy lifting, bending or strenuous activity for 2 weeks
-
Attend scheduled follow-up appointments for cleaning and examination