Adenoid and tonsil enlargement
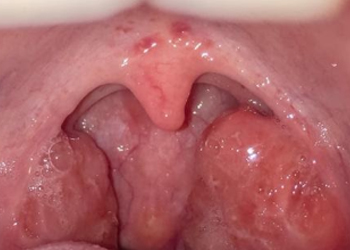
Adenoid and tonsil enlargement
Enlarged adenoids and tonsils are common in children and may cause difficulty breathing, snoring, restless sleep, mouth breathing, recurrent infections and even speech or swallowing issues. When significantly enlarged, they may obstruct the airway, affect sleep quality or contribute to ear problems. Early evaluation helps determine whether medical treatment or surgical removal is needed.
Treatments Offered
We offer complete assessment and treatment options for enlarged adenoids and tonsils:
-
ENT Examination: Assessment of adenoid and tonsil size, airway obstruction and associated symptoms like snoring or recurrent infections.
-
Nasal Endoscopy: A simple endoscopic evaluation to visualise adenoid size and airway narrowing.
-
Hearing & Ear Evaluation: Tympanometry and audiometry to check for fluid buildup or hearing issues caused by enlarged adenoids.
-
Medical Treatment: Nasal sprays, anti-allergic medications or antibiotics when infections or allergies contribute to enlargement.
-
Adenoidectomy & Tonsillectomy: Recommended in cases of airway obstruction, sleep apnea, recurrent infections or persistent ear problems.
When to Seek Evaluation
Consult an ENT specialist if your child experiences:
-
Snoring, noisy breathing or pauses in breathing during sleep
-
Mouth breathing most of the time or persistent nasal blockage
-
Frequent sore throats, tonsillitis or difficulty swallowing
-
Recurrent ear infections or hearing difficulties
Causes may include repeated infections, allergies, environmental irritants or normal lymphoid tissue growth. Identifying the contribution of enlarged adenoids/tonsils helps tailor the best treatment approach.
Management & Long-term Care
Management may include medical or surgical approaches:
-
Nasal saline rinses and anti-allergic medications to reduce inflammation
-
Treating associated allergic rhinitis to relieve nasal blockage and reduce adenoid growth triggers
-
Adenoidectomy or tonsillectomy for airway obstruction, sleep issues or frequent infections
-
Monitoring growth, speech development and ear health as part of follow-up care